The Australian Energy Market Operator (AEMO) has cautioned that the upcoming El Niño summer might lead to a surge in electricity demand, reaching a level not seen in a decade. This increase is anticipated due to the combination of intense heat, severe drought, and bushfires.
Rolling out the 2023/24 Summer Readiness Overview, AEMO Executive General Manager Operations Michael Gatt said the forecast was particularly bleak for Western and Eastern Australia.
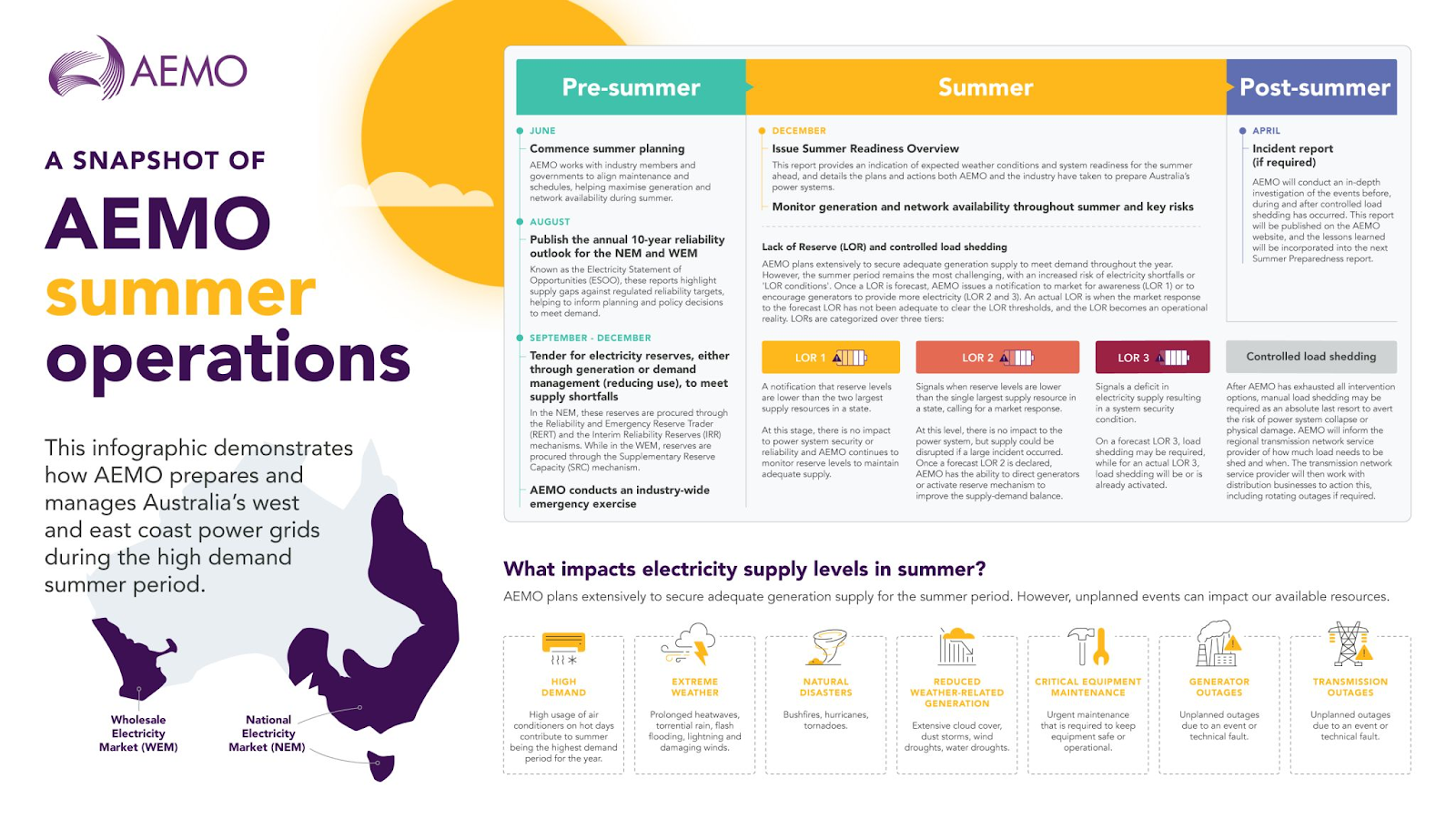
Mr Gatt said AEMO is worried about drought, storms, cyclones, fire hazards, and intense heat.
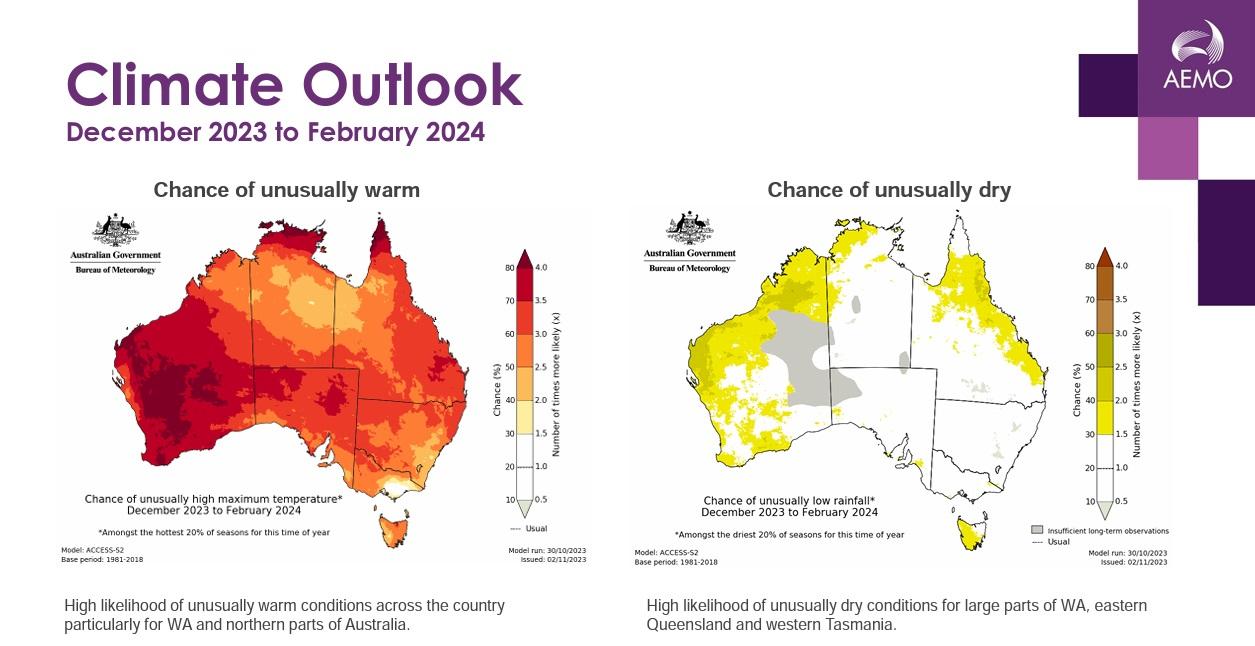
The Bureau of Meteorology predicts abnormally dry and hot weather throughout a significant portion of the country, influenced by the El Niño phenomenon.
AEMO is implementing contingency plans to manage the risks, including seeking an unspecified amount of “short notice” reserve and emergency capacity.
(To get a better idea of what the reserve and emergency capacity is, read our article here.)
This will most likely take the form of demand management – asking big energy users such as refineries and smelters to temporarily reduce their loads at peak demand.
Forced outages likely during periods of low solar and wind
The report indicates that the risk of load shedding (forced outages) persists in regions where high-demand days coincide with low wind and solar availability or scheduled generation and network outages.
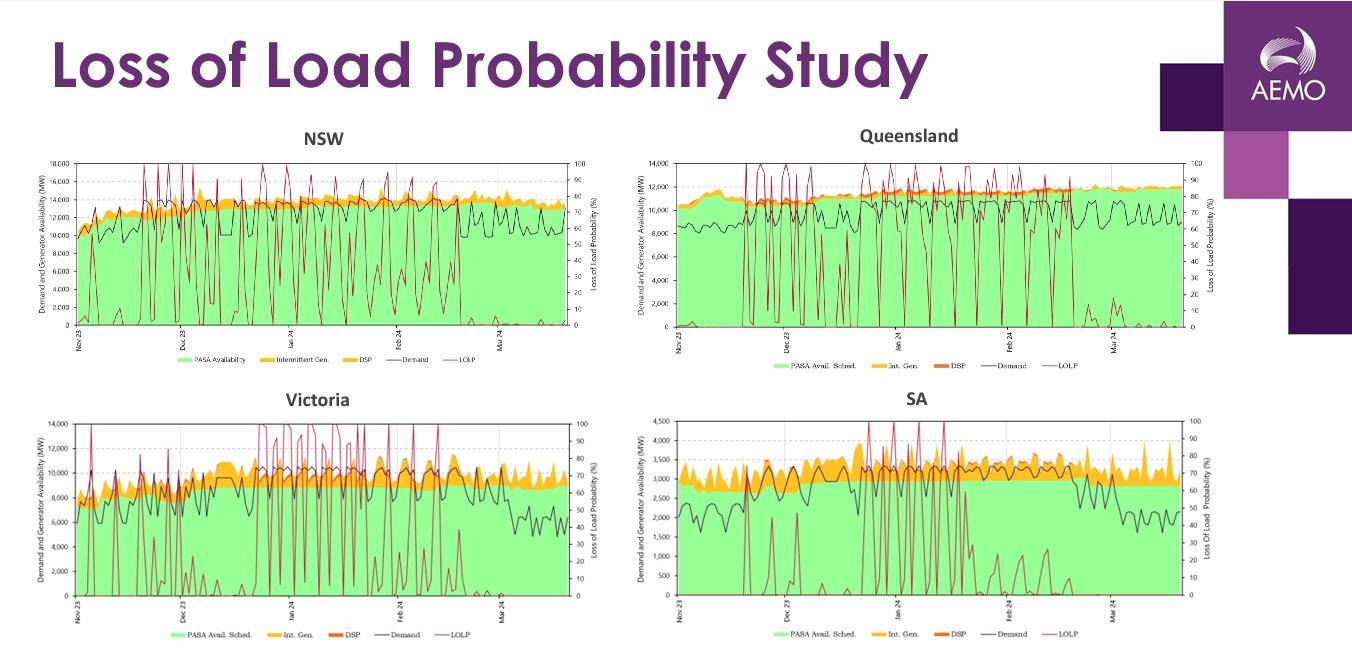
The forecasts, illustrated in the above graphs, anticipate potential load loss in various states throughout the summer.
However, these projections, similar to the 10-year forecasts in the annual Electricity Statement of Opportunities, are presented before any corrective measures are implemented. The short-term Reliability and Emergency Reserve Trader (RERT) tender aims to address and mitigate these risks.
1.5GW of new battery capacity
AEMO’s preparedness is further strengthened by adding 1.5GW of new dispatchable capacity in the past year, primarily in the form of battery storage.
Examples include the Hazelwood and Torrens Island batteries, situated on the sites of former and aging thermal generators, and the Riverina battery.
The summer readiness report mentions the 100 MW, two-hour Capital battery.
However, Neoen has recently reported that it might not be available until early 2024 due to connection issues.
Additional recently installed batteries comprise the Bouldercombe and Queanbeyan batteries and the Kwinana battery in Western Australia.
The 320MW Tallawarra B gas station is also anticipated to come online.
2 GW of new wind and solar power this summer
Gatt also highlighted the availability of 2,000 MW in generation capacity from new wind and solar projects for the upcoming summer.
He said the increased availability of generation and the procurement of additional reserves will assist in managing potential reliability challenges.
13 coal power outages projected
Thirteen units at coal-fired power stations will be offline, primarily during November and December, with some facing extended periods of inactivity.
AEMO has also expressed concerns that Mt Piper may encounter coal supply issues.
The affected units include:
NSW: Bayswater 1, Eraring 2
QLD: Callide B1/B2,C3/C4, Gladstone 1/2 and Tarong 4
VIC: Loy Yang A2, Newport, Yallourn 2
WA: Bluewater U2
Gas and diesel generation outages
East Coast gas usage will need to be monitored. Supply from Queensland may be required due to gas production maintenance outages.
Generation outages include:
NSW: Colongra 3
VIC: Newport, Jeeralang B1
SA: Torrens Island B2, B3 and B4(staggered)
WA: Alinta Wagerup U2, Newgen Neerabup GT
Transmission maintenance outages
QLD: Maintenance/commissioning of 275kV feeders out of Nebo, Broadsound and Strathmore.
NSW: Maintenance of Wagga -Jinderra330kV and Balranald -Buronga 220kV lines.
VIC: maintenance works Heywood –Mortlake and Keilor–South Morang 500kV lines and project works at Red Cliffs (March 2024).
SA: Maintenance activities on South-East to Heywood and South-East to Tailem Bend 275kV lines.
TAS: Maintenance on Gordon to Chapel Street and Sheffield –Farrell 220kV lines.
WA: Muja BTT1 and Muja 132kV Busbar short outages
Multiple VIC-NSW interconnector-related outages are scheduled in February and March 2024.
Restricted hydro and transmission maintenance
Certain hydro capacities will be restricted due to water licenses, dam levels, and riverbank capacity.
Additionally, there may be challenges with gas supplies, particularly from Queensland, due to gas production maintenance outages.
Maintenance is scheduled for multiple transmission lines and state interconnectors at various points.
Extreme climate and weather conditions like El Niño can affect electricity generation, demand, and prices which, in turn, can heavily impact consumers, especially businesses with large consumption. To help soften the blow of this uncertainty, take control of your business’s energy use and costs. Our Energy Management Consultants can guide you through the process of optimising your electricity consumption and costs and help you meet your energy goals.
Get started with obligation-free electricity tenders for your business here.
To read the complete 2023/2024 Summer Readiness – Overview by AEMO, click here.






